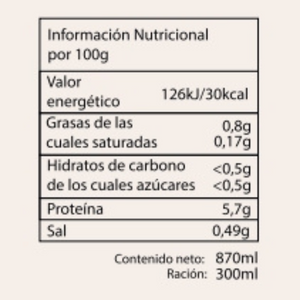
The ketogenic diet , also known as the Keto diet , is a diet low in carbohydrates (sugars, cereals, legumes, fruits, tubers) and high in fats (avocado, olive oil, olives, coconut, ghee).
In general, carbohydrate intake should be reduced to 20-40 g daily. At the macronutrient level it would be: 5%-10% carbohydrates, 15-25% proteins and 65-70% fats.
The main objective of the keto diet is to ensure that our body does not depend on glucose as a source of energy and can draw on fat reserves instead (producing ketone bodies).
One of the reasons why it has so many followers is that it is very satiating, thus facilitating the calorie deficit. In addition, this diet manages to recover metabolic flexibility and stimulate the use of fat as an energy substrate.
What is metabolic flexibility? It is the ability of our body to use one energy substrate or another according to our need or availability. Having metabolic flexibility helps us perform more, burn fat more easily and have an optimal immune response at all times.
However, conventional diets and modern lifestyles create the opposite: metabolic inflexibility. We don't move, we are constantly stressed and we don't stop eating (especially processed products and carbohydrates). This causes us to continually have high insulin and hardly use our fat reserves, which will end up leading to much worse problems such as metabolic syndrome (obesity, insulin resistance, hypertension...)
Benefits of the KETO DIET
The keto diet has been used since 1920 as a treatment for epilepsy, progressively gaining importance and becoming more widespread. And its effect that enhances mitochondrial respiration against glycolysis for energy metabolism greatly expands the range of pathologies in which it can be effective in both children and adults. Recent studies have shown a therapeutic effect of the keto diet in several pathological conditions such as obesity, diabetes, PCOS, cancer and the improvement of cardiovascular risks and certain neurodegenerative diseases.
Obesity
There is solid evidence that the use of the ketogenic diet in weight loss is effective , although there are several theories about the mechanisms that make it work. Some studies suggest that there are no metabolic advantages to low-carbohydrate diets and that weight loss derives from a calorie reduction, probably due to the satiating effect of protein. However, there are studies that support the hypothesis that there is a metabolic advantage.
We can summarize the weight loss effects of ketogenic diets:
- Reduction of appetite due to the satiating effect of proteins, effects on hormones that control appetite and a possible appetite suppressing effect of ketone bodies
- Reduction of lipogenesis and increase of lipolysis
- Reduction of the respiratory quotient at rest, and, consequently, increase in fat oxidation.
- Increased metabolic costs of gluconeogenesis and thermic effect of proteins
Cardiovascular risk
Several studies show that reducing carbohydrates to levels that induce a state of ketosis can provide significant benefits to the lipid profile. Studies suggest that ketogenic diets reduce triglycerides, total cholesterol and increase HDL.
Type 2 diabetes
Insulin resistance is nothing more than a “carbohydrate intolerance.” When carbohydrate intake is restricted, the signs and symptoms of insulin resistance tend to disappear. Improvement in glycemic control, glycosylated hemoglobin and lipid markers as well as reduction or even withdrawal of insulin occur even before the patient loses weight.
Individuals with metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes generally see objective and symptomatic improvements in risk biomarkers if they follow a well-formulated very low carbohydrate diet. Glucose control improves not only because there is less glucose in the body but because insulin sensitivity also improves.
Epilepsy
The effectiveness of the ketogenic diet in epilepsy is strongly supported by a Cochrane review where all studies showed a 30-40% reduction in seizures compared to control groups and, in children, the authors confirmed that the effects of the ketogenic diet They were comparable to antiepileptic drugs.
Cancer
Perhaps due to glucose starvation of cancer cells and a reduction in the proliferative effect of insulin, the ketogenic diet could help in the treatment of certain types of cancer, although more research is required.
PCOS
Women with PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome) frequently show signs related to metabolic syndrome such as insulin resistance, obesity, type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia and also high levels of inflammation. Some of the suggested treatments are those that increase insulin sensitivity such as lifestyle changes (diet and physical activity) and pharmacological treatments such as metformin. It is evident that any intervention that improves insulinemia and reduces weight can be effective in reducing androgenism, normalizing ovulation, and reducing several symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome.
Neurological diseases
Studies suggest the use of the ketogenic diet as a therapy for several neurological diseases such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, autism and multiple sclerosis. Although they are different diseases, the effectiveness of the keto diet lies in the neuroprotective effect in any disease whose cause is related to abnormalities in the use of cellular energy (a common characteristic in neurological disorders). The exact mechanism is still unknown, although several studies suggest possible reasons:
- Ketone bodies act as neuroprotective agents by increasing ATP levels and reducing reactive oxygen species in neurological tissues, along with mitochondrial biogenesis, which could help regulate synaptic function.
- The increased synthesis of polyunsaturated fatty acids stimulated by a ketogenic diet could play an important role in neuronal membrane excitability.
- The possibility is also being considered that the reduction in glucose metabolism thanks to the ketogenic diet could activate anticonvulsant mechanisms.
- Furthermore, the caloric restriction usually induced by the ketogenic diet could have neuroprotective effects such as improvement in mitochondrial function, reduction of oxidative stress and apoptosis, as well as inhibition of pro-inflammatory mediators.
ALLOWED FOODS AND THOSE YOU SHOULD AVOID:
First of all, and this applies to ALL DIETS. You have to eat food and not products. No matter how keto, low carb they are, it is better to always eat foods rich in nutrients that come from nature and avoid processed foods.
That said, if you want to follow a Keto diet you should keep the following in mind:
- The main protagonists of the keto diet are FATS, although not just any fat, try to avoid trans fats, margarines and refined oils. Choose healthy fats such as extra virgin olive oil, virgin coconut oil, olives, avocados, ghee, homemade mayonnaise or pesto sauce, eggs, oily fish, seeds and nuts (although not all as there are some with high levels of carbohydrates such as cashew or pistachio).
- PROTEINS are allowed: red meat, poultry, pork, organ meats, shellfish, white and blue fish, eggs and fermented dairy products.
- CARBOHYDRATES are limited. You should avoid sugars, flours, cereals, legumes, tubers, fruits (only strawberries, blackberries, blueberries, lemons, limes, tomatoes and coconuts are allowed in small quantities) and vegetables with a high glycemic index ( pumpkin, beet, carrot).
- The vegetables that are allowed and should be part of a healthy keto diet are chard, spinach, broccoli, cauliflower, brussels sprouts, red cabbage, kale, zucchini, lettuce, endives, artichoke, arugula, lamb's lettuce, radish, watercress. , zucchini, eggplants, cucumber, peppers, asparagus, thistle, borage, celery, mushrooms... Garlic, onions, leeks, chives and spring garlic should be moderated.
Side effects of the Ketogenic diet
The ketogenic diet can have several side effects that usually reverse within a week:
- Keto Flu
- Bad breath
- Constipation
1. “Keto Flu”:
Keto flu causes one or more of these symptoms: Tiredness, headache, irritability, dizziness, muscle cramps, nausea.
Keto flu is caused by the transition that occurs when the body begins to burn fat for energy instead of sugar. When insulin levels drop, the body reacts by excreting more sodium in the urine along with water. Because of this, you usually urinate more often during the first days or even the first week of ketogenic eating. That loss of water and sodium is what causes many of the unpleasant symptoms of the keto flu. That is why it is advisable to drink salt or sea water while following a ketogenic diet.
At Cooldo we recommend drinking bone broth that will help remineralize and replenish sodium deposits. It's a delicious way to reverse the keto flu.
Anyway, most people feel some of these symptoms during the first week, but as soon as the body adapts to the ketogenic diet these symptoms disappear. In fact, you usually have more energy than before starting the diet.
2. Bad breath
When you enter ketosis, the body uses fat reserves for energy. Fatty acids are converted to ketones, which are natural chemicals such as beta-hydroxybutyrate, acetoacetate, and acetone. Ketones are released from the body through exhalation and urine and have a particular odor that is often reminiscent of nail polish remover (which contains acetone). But do not worry! Bad breath usually does not last more than a week, which is how long it takes for the body to adapt to the change in diet. Furthermore, not everyone experiences bad breath, it is a very bio-individual thing.
3. Constipation
Constipation on ketogenic diets can occur for two main reasons:
- Dehydration and lack of lubrication in the stool:
Low-carbohydrate ketogenic diets have a diuretic effect that can lead to constipation. Drinking enough fluids daily can help you stay well hydrated and make your stools softer. We recommend you hydrate with water with minerals, bone broth and infusions and avoid carbonated and/or sugary drinks.
- Reduced fiber consumption:
On the ketogenic diet there is usually a considerable decrease in daily fiber intake. It is important to eat low-carb vegetables to achieve optimal levels. Include a minimum of 1 to 2 cups in each of your meals to increase your fiber intake and relieve constipation. You can also supplement your diet with psyllium husk, flax seeds, chia seeds if you feel you need more fiber. These concentrated sources of fiber are low in carbohydrates and can be added to a salad, yogurts, smoothies or mixed with water. Our favorite remedy for constipation is to hydrate psyllum, chia or flax seeds in water and drink them before going to bed. It is a super effective remedy. And if you need extra help, add a tablespoon of magnesium carbonate.